What Does R Stand For in Insulation?
R-Value is the rating system used to grade insulation products or a material's insulating properties. The "R" stands for "resistance" and refers to a material's resistance to heat flow, or temperature conduction.
What Is The R-Value?
The "R" in R-value stands for resistance—specifically, resistance to heat flow. R-value is a universal rating system that measures how well an insulation material resists temperature conduction. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation is at keeping heat in during winter and out during summer.
Key Facts About R-Value
R-Value and Energy Efficiency
A higher R-value means more effective insulation, which translates into energy savings and lower utility bills. Proper insulation keeps your home comfortable year-round while reducing the strain on your heating and cooling systems.
R-Value and Location
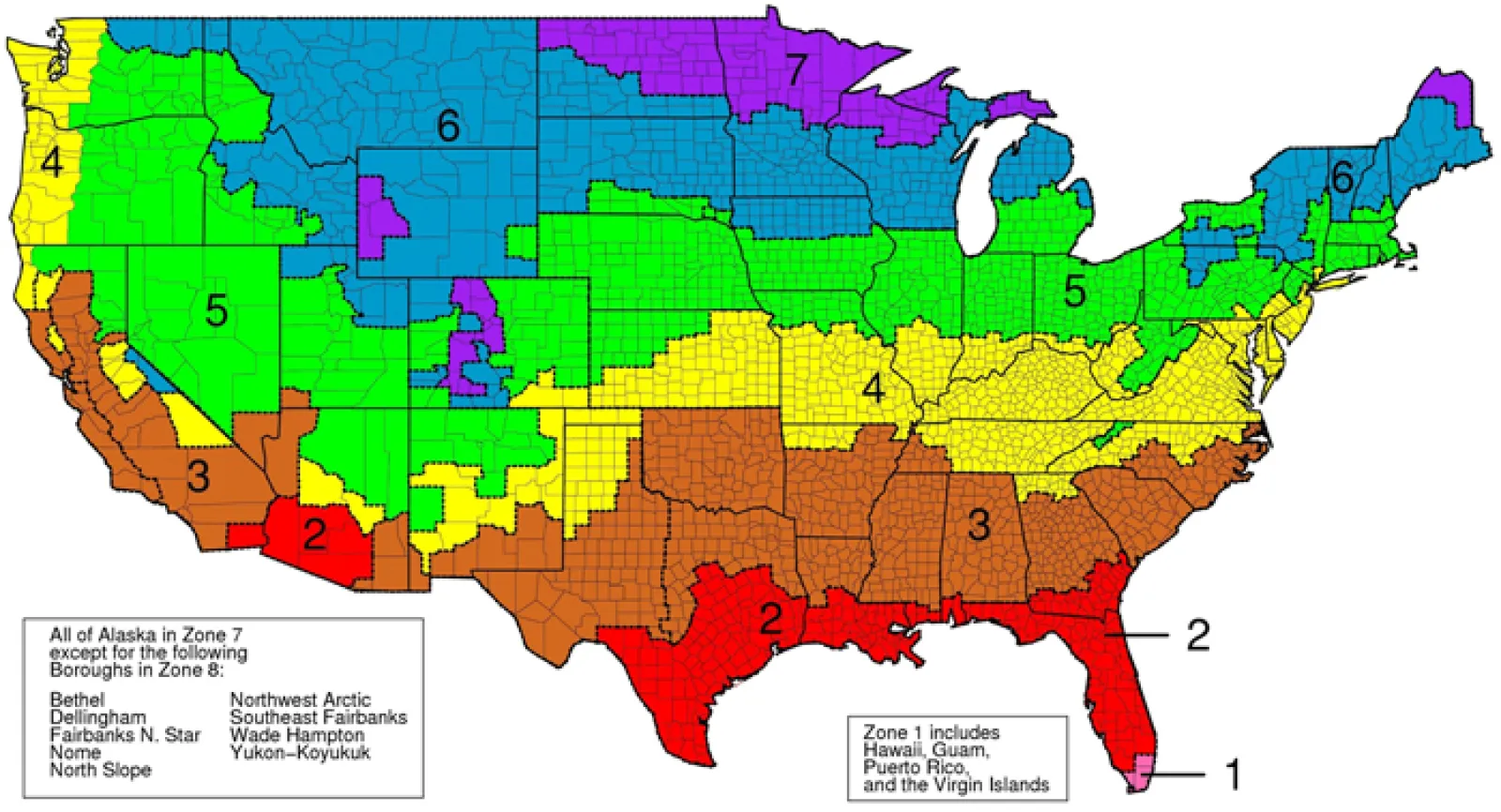
Your ideal R-value depends on where you live and your home's structure. For instance, a home in a colder climate will require insulation with a higher R-value compared to one in a warmer region. The U.S. Department of Energy provides a helpful map with recommended R-values based on your geographic area.
R-Value and Insulation Type
Not all insulation is created equal when it comes to R-value representation. Batt insulation often lists its R-value in the product name, making it easy to identify. In contrast, spray foam insulation indicates its R-value per inch, requiring a bit more calculation to determine the total insulation value.
How Much R-Value
Should My Insulation Have?
Choosing the appropriate R-value for your home's insulation is crucial for energy efficiency. The United States Department of Energy provides a map outlining recommended R-value ranges for different regions:
Southern States:
- Attic insulation: R30 to R60
- Floor insulation: R13 to R19
Northern States:
- Attic insulation: R49 to R60
- Floor insulation: R25 to R30
If you're adding new insulation to existing layers, you might not need the full recommended R-value since your home already has some protection.

USA Premium Foam® has the
highest R-Value in its class.
Now that you know what R-Value is, how does our premium insulation product compare? Our proprietary USA Premium Foam Insulation has a superior R-Value of 5.1 per inch, which is 35% higher than any retrofit stud wall application. In fact, it's the highest on the market.
Our product's R-Value is higher than:
-
Rigid panels
-
Other spray foam insulation
-
Rockwool
-
Fiberglass
-
Cellulose
-
Blown-in insulation

*This is a representation only and may not be exact.
Is my home's R-Value high enough?
The United States Department of Energy warns homeowners that just 1 in 5 homes constructed prior to 1980 are sufficiently insulated. While homes constructed today are required to meet R-Value standards set by the U.S. Department of Energy, this requirement was not included in building codes prior to the mid-1970s. This means that approximately 80% of homes built before this time are in need of better insulation! If you're uncertain if your home falls within this category, contact us and our energy experts can help you determine if you're in need of insulation.
Find the R-Value Standards for Your Region
FAQs
The higher the R-value, the better the insulation is at insulating a home. Typically, materials with higher R-values are more expensive than those with lower R-values.
What Is A Good R-Value For Insulation?
The recommended R-Values for insulation vary depending on your location and the area of your home being insulated. For exterior walls, R-13 to R-23 is typical, while R-30, R-38, and R-49 are common for ceilings and attics.
What Does R Stand For In R-Value?
What is the meaning of the "R" in R-Value? The recommended R-Values for insulation can vary depending on the location and specific area of your home that is being insulated. R-13 to R-23 is typically recommended for exterior walls, while R-30, R-38, and R-49 are common for ceilings and attics.
Can You Over Insulate A Home?
Yes, the purpose of home insulation is to create a tight seal, but if you add too many layers of insulation, moisture can become trapped and lead to mold growth.
















